


Graphite and diamond are examples of giant covalent structures. Some solids can turn straight into a gas, skipping the liquid phase this is called sublimation. Gases can be turned back into liquids by condensation, lowring the amounf of energy particles have. Liquids can turn into gases by evaporation or boiling (again by increasing the energy of the particles). Liquids can be turned back into solids by freezing, lowering the amount of energy particles have. This involves increasing the energy of the particles normally by heating. Solids can turn into liquids through the process of melting. Changing from one state to another is a physical change as you end up with the same chemical as you began with (whereas a chemical change would lead to different chemicals). Some of the forces need to be broken during melting, whereas all of the forces must be broken during evaporating/boiling. The amount of energy required to change state depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces between the particles of each substance. To get from a solid to a liquid, or a gas, energy has to be supplied - usually through heating. During these changes the particles gain energy, which is used to break or overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction.įluids (liquids and gases) are able to take the shape of their containers, however, only gases can be compressed as their particles are far apart and have space to move into. Particles in solids have less energy than liquids, which in turn have less energy than gases.

In these diagrams, particles are represented by solid spheres. These kinds of bonds occur mainly between a metallic and a non metallic atom.Solids (s), liquids (l) and gases (g) can be represented using particle diagrams. Ionic bond, also known as electrovalent bond, is a type of bond formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound. These two opposite ions attract each other and form the ionic bond.Ĭovalent bonding is a form of chemical bonding between two non metallic atoms which is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms and other covalent bonds. Non-metals(-ve ion) are "stronger" than the metal(+ve ion) and can get electrons very easily from the metal. For stabilization, they share their electrons from outer molecular orbit with othersĪn ionic bond is formed between a metal and a non-metal. Neither atom is "strong" enough to attract electrons from the other. The bond between these two ions is called an ionic bond.Ī covalent bond is formed between two non-metals that have similar electronegativities. This results in a positively charged ion (cation) and negatively charged ion (anion). If two atoms differ considerably in their electronegativity - as sodium and chloride do - then one of the atoms will lose its electron to the other atom. the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Whether two atoms can form a covalent bond depends upon their electronegativity i.e.
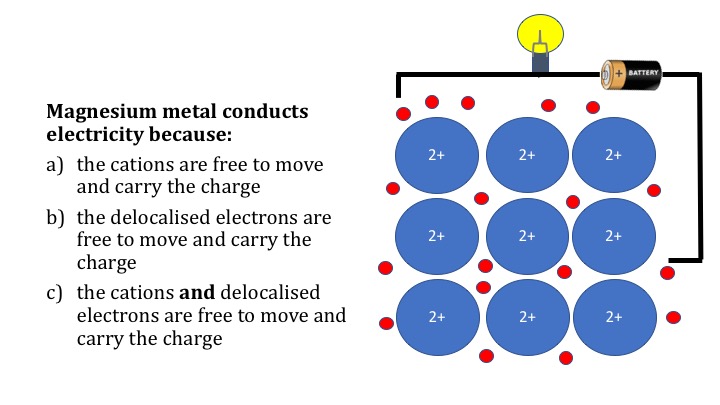
Relatively high energies are required to break them (50 - 200 kcal/mol). Covalent bonds consist of pairs of electrons shared by two atoms, and bind the atoms in a fixed orientation. They differ in their structure and properties. There are two types of atomic bonds - ionic bonds and covalent bonds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
